Culturally, we’re obsessed with our appearance and a huge topic in regards to our appearance is body fat. Body fat, although a essential part of normal body function, has become a huge problem for a country with rising obesity rates. In response, more and more research has gone into understanding the way our bodies store and process fat.
The traditional understanding of fat and its role in the body has fallen by the wayside as research reveals that fat’s relationship with our health and appearance is much more complicated than we first thought.
What is fat?

A growing body of research is showing us that not all fats are created equal and the way the human body processes different types of fat has greater importance than previously thought. To further complicate the matter, the way an individual’s body stores fat is impacted by a wide variety of factors beyond simply diet and lifestyle. Gender, age, genetics, and hormones also play important parts in the manner that fat is stored in the body.
Types of Fat and Body Shape
Healthy eating habits, regular exercise and proper management of health are important aspects of wellness and overall health. However, those who work out and eat healthy may eventually realize that their goals of a leaner, tighter body mysteriously remains out of reach.
Each type of fat has a unique molecular structure, characteristics, and impact on health.
At the heart of this issue are body composition and body shape. For many individuals, even though the numbers on the scale are within a reasonable range of their ideal weight, they may not be seeing the results reflected in their appearance. There are many different factors that go into body composition and the state of your physique.
Types of fat:
- Brown Fat
- Subcutaneous White Fat
- Beige Fat
- Subcutaneous Fat
- Visceral
Brown fat
Brown fat is regarded as a beneficial type of fat that can be stimulated to burn calories. Studies of individuals with leaner body composition demonstrate a greater concentration of brown fat. Some scientists are even looking into brown fat therapies as a means of obesity treatment! Brown fat shows more predominantly in children and decreases as you age. Generally, the concentration of brown fat in the body is a small percentage relative to white fat. For example, a healthy individual may have a total of twenty pounds of fat, but of that, only three ounces of it will be brown fat. However, the three ounces of fat is capable of burning an additional 400 calories per day when in “activation.”
White Fat
White fat appears in larger quantities in the body and functions as a storage unit for energy. White fat also secretes an essential hormone called adiponectin, which helps regulate the liver’s insulin sensitivity and protect against heart disease. When white fat concentrates in larger amounts, some of its protective characteristics diminish.
When you gain weight, white fat collects in greater concentrations, which exacerbates the slowdown of adiponectin secretion, which subsequently leads to additional fat storage around the hips, thighs, and abdomen. White fat deposits in these areas are especially challenging to remove through dieting or exercise.
Fat Location
The location of fat in the body also plays a part in its effect on your health and appearance. There are two main categories that describe where fat is located in your body, visceral and subcutaneous.
Visceral Fat
Studies show that 30 minutes of moderate activity each day can have a significant impact on the percentage of visceral fat in your body.
This type of fat is located deeper in the body, positioned around abdominal organs and collected in spaces between the organs. Visceral fat poses greater risks to your health due to its negative influences on blood pressure and links to sleep apnea. The amount of visceral fat in the body is determined by a number of factors such as age, gender, and genetic history. Although visceral fat is known to be a greater danger to your health, it is also much easier to lose through healthy living and exercise.
Visceral fat tends to concentrate around the abdominal area and is usually what people think of when they say “belly fat.” Studies of visceral fat and diet note that eating fewer simple carbohydrates such as refined pasta and sugary drinks can reduce visceral fat.
Subcutaneous Fat
Dieting and exercise can impact the amount of fat stored across the entire body, but the body will resort to reducing stores of visceral belly fat first.
Subcutaneous fat is adipose tissue that is stored close to the surface of our skin. This is the type of fat that generally has an immediate impact on the body’s appearance. Unfortunately for those who wish to achieve leaner, sculpted bodies, subcutaneous fat is notoriously difficult to reduce through diet and exercise. Subcutaneous fat is the body’s natural emergency store of energy reserves, the evolutionary result of our long, ancient history of food scarcity.
Subcutaneous fat is usually what people are observing when conducting “pinch tests” or referring to stubborn pockets of fat.
Alpha and Beta Receptors
One of the most recent discoveries about fat is that there are two types of “fat receptors,” Alpha and Beta. These receptors manage your body’s blood flow and fat burning capabilities. Alpha receptors decrease while beta receptors increase. The number of alpha and beta receptors is decided at birth and research indicates that individuals with high numbers of alpha receptors struggle to lose fat.
Lipedema

Lipedema is more common than once believed, occurring in as many as 11% of adult women. Lipedema disproportionately affects women and rarely appears in men. Those who are otherwise healthy may experience emotional distress and anxiety caused by the impact of lipedema on their appearance.
How to Lose Fat?
For improving your overall health, reducing the amount of fat stored in the body is essential. Although exciting new studies have gone into developing brown fat triggers and drug-based treatments to target abdominal fat, the tried-and-true methods are physical activity and eating right.
Many individuals with body goals tend to fixate on the number they read on their scale. However, the amount your body weight is not necessarily the best indicator of your health. The Body Mass Index, BMI, is a more accurate measure.
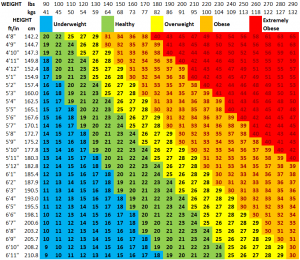
That said, even an accurate BMI reading does not tell the full story. The relative concentration of fat in your body is ultimately hard to determine. For example, those with muscular, athletic bodies may weigh more and have a higher BMI reading for someone of their size. More and more health experts, nutritionists and dieticians are saying that factors such as feeling good, feeling confident, eating healthy and regular exercise are far more important for health and wellness than the number that reads on the scale.
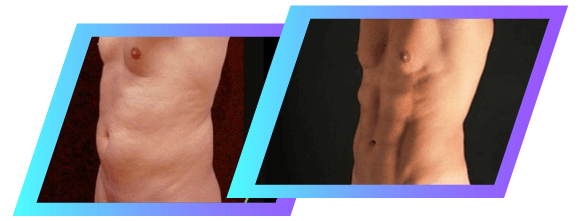
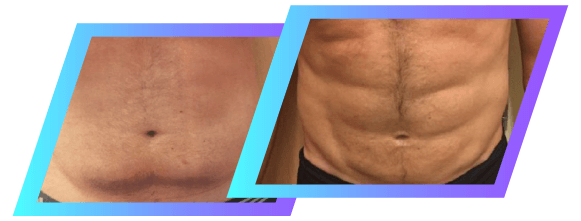
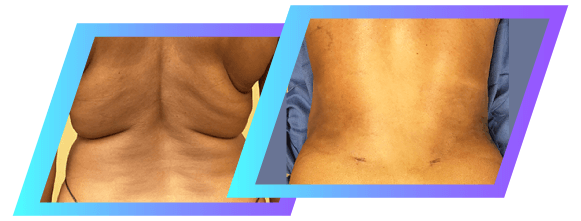
Body Sculpting
Even with appropriate levels of exercise and careful dieting, many individuals struggle to reduce fat deposits on their body. Trouble spots and stubborn fat deposits can frustrate even your best efforts, making your body goals feel out of reach.

Liposuction and Vaser Liposuction treatments are minimally-invasive and require relatively little recovery time. Those with conditions such as lipedema may also find lasting relief from their symptoms with surgical intervention.
Liposuction treatment delivers results quickly and has a consistently high satisfaction rating. Patients who choose liposuction often go on to further improve upon their dieting and exercise habits.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Jack Friedlander to learn more about how to achieve your body goals.